16 September، 2025
Master thesis discusses the diagnosis of bacteria isolated from cases of bacteremia
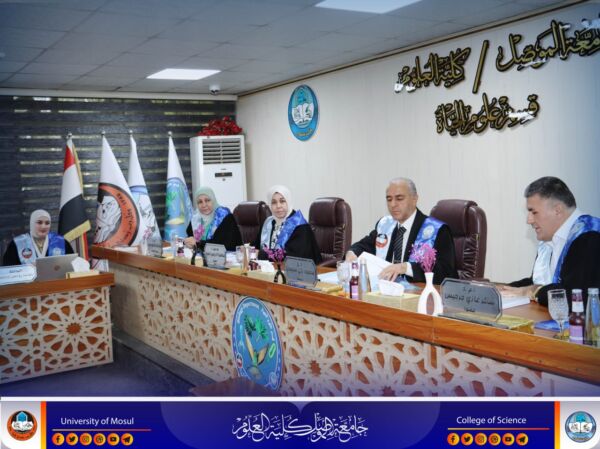

The Department of Biology at the College of Science – University of Mosul discussed the master thesis tagged “diagnosis of bacteria isolated from cases of bacteremia and inhibition of gene expression of anti-flux genes of the most isolated bacteria” on Tuesday, September 16, 2025, in the presence of the head of the Department, Professor Dr. Amjad Abdul Hadi and a number of teaching and graduate students.
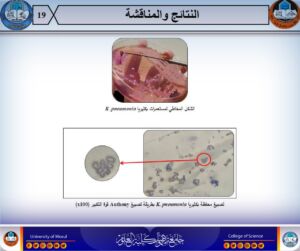
Student Rasliya Yunus Mahmoud Ahmed from the microbiology branch presented an integrated study focused on revealing the ability of Klebsiella pneumoniae strains to produce signal molecules within the Quorum Sensing (QS) phenomenon, in addition to investigating the effect of different concentrations of vitamin C in inhibiting the production of these molecules through the Quorum Quenching (QQ) phenomenon. The study also for the first time locally adopted the PFGE technique to determine the genetic relationship between strains and the source of infection.
The most notable objectives of the study included :
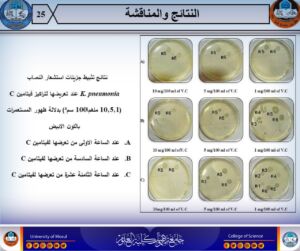
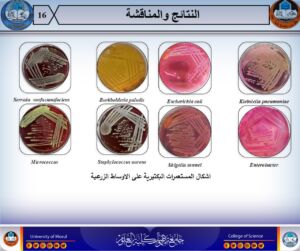
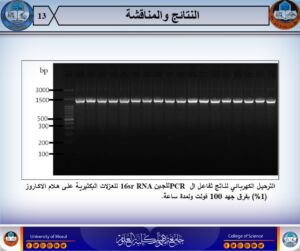
- Isolation and diagnosis of bacteria from cases of bacteremia using 16S rRNA assay.
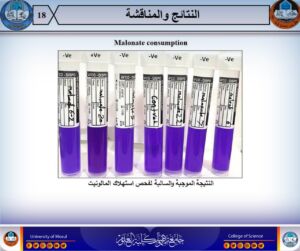
- Subtype identification of the most dominant pneumoniae strain via the Voges-Proskauer and malonite consumption tests.
- Evaluation of the effect of bacteremia on kidney and heart function by laboratory tests of their serum levels.
- Detection of quorum sensing phenomenon and the ability of strains to produce long-chain signal molecules.
- To investigate the effect of vitamin C at different concentrations on the inhibition of the production of signaling molecules within the Quorum Quenching phenomenon.
- Determination of the serotype of the pneumoniae wallet using PCR technology to find out the dominant pattern.
- Conducting genotyping of local breeds using PFGE technology and drawing up the genetic tree to clarify the extent of genetic affinity and the source of infection.
The discussion Committee was chaired by Dr. Mahmoud Zaki Suleiman Sultan, and the membership of assistant professor Dr. Shaker Ghazi jerjis Hussein and Dr. Sahra Idris Hamid Ahmed, under the supervision and membership of assistant professor Dr. Ghada Abdul Razzak Mohammed Ibrahim.
Sustainable development goals aligned with the mission :
- Goal 3: good health and well-being : the thesis promotes the understanding of bacterial infections and bacteremia, contributing to the development of diagnostic and treatment methods, improving the health and well-being of patients.
- Goal 9: Industry, Innovation and infrastructure : the use of modern technologies such as PFGE and PCR for the first time locally reflects a scientific innovation in the field of medical microbiology.
- Goal 4: quality education: preparing and discussing the thesis raises the level of specialized education and training for graduate students in life sciences and microbiology.
- Goal 17: Partnerships for goals: the study supports cooperation between researchers and laboratories, the exchange of knowledge and scientific experiences locally and internationally.
This study is an important scientific step to enhance the scientific understanding of the behavior of K-strains. pneumoniae in cases of bacteremia, opening up new horizons for the development of strategies for inhibiting its molecular activity, thereby contributing to supporting scientific research efforts and microbiological control locally.
Our wishes to our dear students continued success and success
Information and Government Communication Division
Tuesday, September 16, 2025